By Bennett Sherry, OER Project Team
Maine, USA
When you tell someone about your day, where do you start? What elements do you focus on? What about the story of your life?
I’m willing to bet that your stories emphasize movement. Where did you go? How did you get there? Where are you from? What journeys changed your life, and what people did you meet along the way? When you ask your students to envision their future, do they talk about where they’ll stay, or where they’ll go?
One of our favorite tools for teaching history is the map. Maps seem like such a solid representation of the complexity of history. They have these clear, unmoving parts: cities, states, natural geography. But maps are only a snapshot of time. Within and among those cities and states and points on any historical map, humans were constantly in motion, changing that map. Some of that movement was just traveling, pilgrimage, or trade. But some was migration.
Migration is a fundamental pattern in human history. A world history of movement reveals linkages and interactions, helping us understand the big patterns and systems that transformed our societies in the past, and which govern our lives in the present. As our world grows more interconnected—as travel and communication technologies proliferate—understanding the history of where we went is critical to figuring out where we should go.
We know that our species began its migration out of East Africa around 70,000 years ago. By 12,000 years ago, humans had crossed seas and mountains and deserts to live on every continent. For most of our history as a species, we were defined by our movement. Bands of foragers moved from site to site, following animal migrations and seasonal weather patterns. Yet, when some foragers became farmers, patterns of human movement didn’t stop—they changed. And they have continued to change. Ever since humans built the first cities, people have moved from rural to urban areas. But not until the twenty-first century did more people live in urban areas than in rural communities.
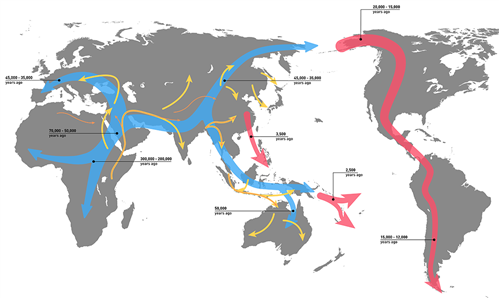 Dispersal routes of early humans. By WHP, CC BY-NC 4.0.
Dispersal routes of early humans. By WHP, CC BY-NC 4.0.
Cross-community migration has been one of the most important drivers of historical change. As the webs of human networks thickened, societies exchanged goods, ideas, and people. Merchants, missionaries, diplomats, bureaucrats, soldiers, and sailors all connected different communities through the exchange of goods, ideas, violence, and disease. Enslaved people and refugees have been forced to leave their homes for most of recorded history. With the expansion of European colonialism and the rise of the plantation system, millions of Africans were enslaved and forced to migrate across the Atlantic Ocean.
People migrate for many different reasons, but for most voluntary migrants, choice to move is motivated by a desire to improve their material conditions—increasing incomes, finding safer living conditions, or accessing new opportunities. After the Industrial Revolution and the steam engine transformed humanity’s ability to travel and communicate, tens of millions of people left their homes in Europe and Asia to seek a better life, many in the Americas. Many of these migrants, and Asian immigrants in particular, faced xenophobia and racism in their new homes.

 Two examples of racist, anti-Chinese cartoons in the United States.
Two examples of racist, anti-Chinese cartoons in the United States.
Top: A political cartoon from the First Red Scare. Public domain.
Bottom: "Immigration East and West". Public domain.
Histories of migration can reveal the origins of power structures we take for granted. Rulers and elites have historically been uncomfortable with the idea of free movement. There's a reason that chains are a universal symbol of oppression. Migration is a choice that shows the agency of normal people—reshaping the world through the simple act of voting with their feet.
Students often don’t realize the complexity of the history of migration. They tend to assume things always were as they are today. Take for example the modern phenomenon of international border controls. Today, we’re used to the idea of restricting migration across national borders using check points, passports, and visas. But the world was not always this way. In his book, Melancholy Order, historian Adam McKeown argued that our international system of migration control and travel documentation developed because white settler nations wanted to limit immigration from Asian countries in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Our international system of migration regulation emerged because of racist policies designed to exclude Asian immigrants.
You’re probably reading this in the year 2020 CE, which means you’re all too familiar with the ways that migration has become a controversial topic. In Europe and the United States, anti-migrant sentiment and policies have increased as nationalist politicians try to scapegoat immigrants for their society’s problems—whether terrorism, economic recession, or the spread of the coronavirus. Migrants are accused of being lazy, dangerous, or leeching off the social safety net. This is despite significant evidence and general agreement among conservative and liberal economists that immigrants are beneficial to their new countries, boosting GDP and starting businesses.
Migration is a long thread in the history of the human past, but it is a thread that constantly changes. Today, patterns of migration continue to evolve. Climate change has already produced refugees fleeing rising sea levels, drought, and extreme weather. Transportation technology allows unprecedented levels of mobility. And digital tools are reshaping our understandings of place, work, and community.
As you think about teaching a history of movement to your students, you might ask them to reflect on how their lives changed with the limits that quarantine has placed on their own mobility. You might also ask them to reflect on how their life story is a product of migration. Do they begin this story 13.8 billion years ago? Seventy thousand years ago? With the arrival of their migrant ancestors? These questions can help them reflect on the ways that their ancestors’—and perhaps their own—migration choices changed history and could change the future.
About the author: Bennett Sherry holds a PhD in history from the University of Pittsburgh and has undergraduate teaching experience in world history, human rights, and the Middle East. Bennett writes about refugees and international organizations in the twentieth century. He is one of the historians working on the OER Project courses.
Cover image: Migrants stranded in the Strait of Gibraltar. Ó Getty Images / MARCOS MORENO.
 For full access to all OER Project resources AND our amazing teacher community,
For full access to all OER Project resources AND our amazing teacher community, 
Top Comments